
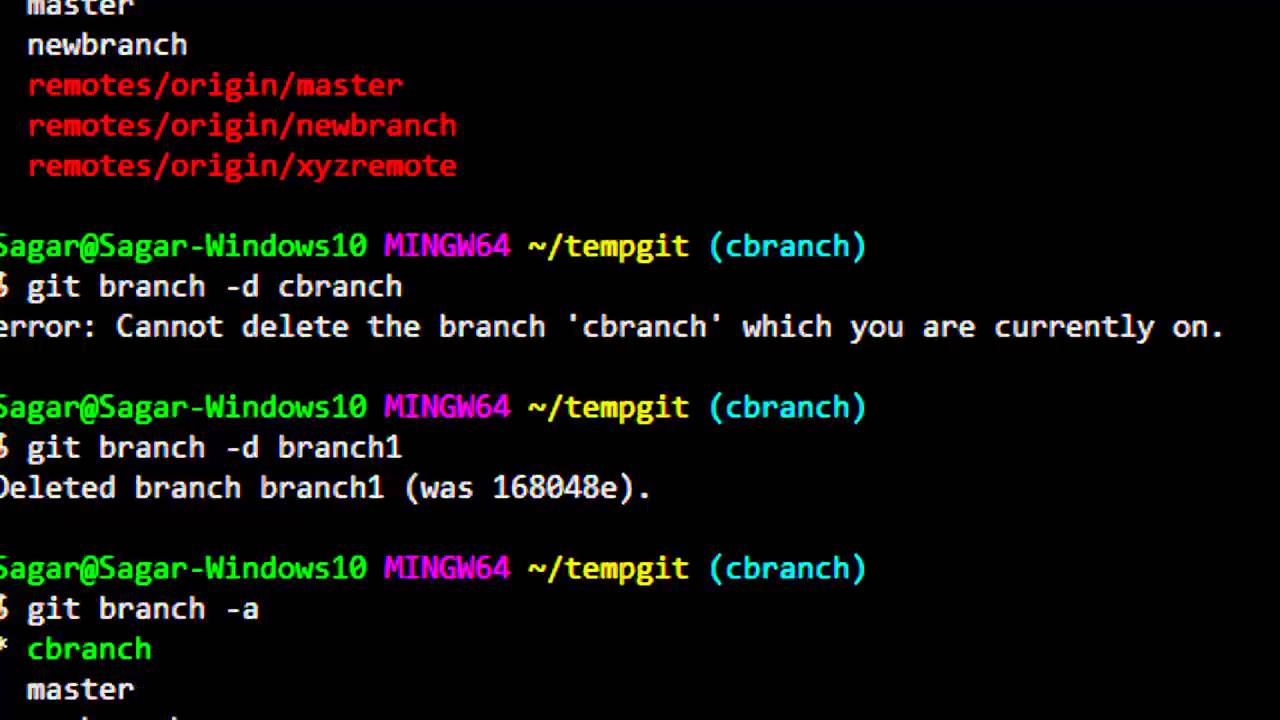
However, the main branch still points toward the C1 commit. This can be achieved using the ` git checkout` command.Īs you can see, when the new commit was created, the HEAD pointer changed its reference and now points toward the latest commit, C2. Here, the HEAD is not referencing or pointing to the main branch instead, it is pointing directly to the C1 commit.
In the image above, the HEAD is pointing to the main branch and the main branch is pointing to the C1 commit. To better understand this, consider an example: This state is known as detached HEAD state. However, it can also point directly to a commit. Thus, the ` HEAD` pointer indirectly points to a particular commit. It is like a pointer that points to a branch, and that branch itself points to a particular commit. ` HEAD` is primarily a reference to a named branch in a Git repository. Reflogs are useful in various Git commands, to specify the old value of a reference.”īefore diving further into the `git reflog` command, let’s take a look at some basics of Git. “ Reference logs, or “reflogs,” record when the tips of branches and other references were updated in the local repository. This command is used to get a record of references to the tips of branches and commits that have been updated.
Github desktop delete local branch how to#
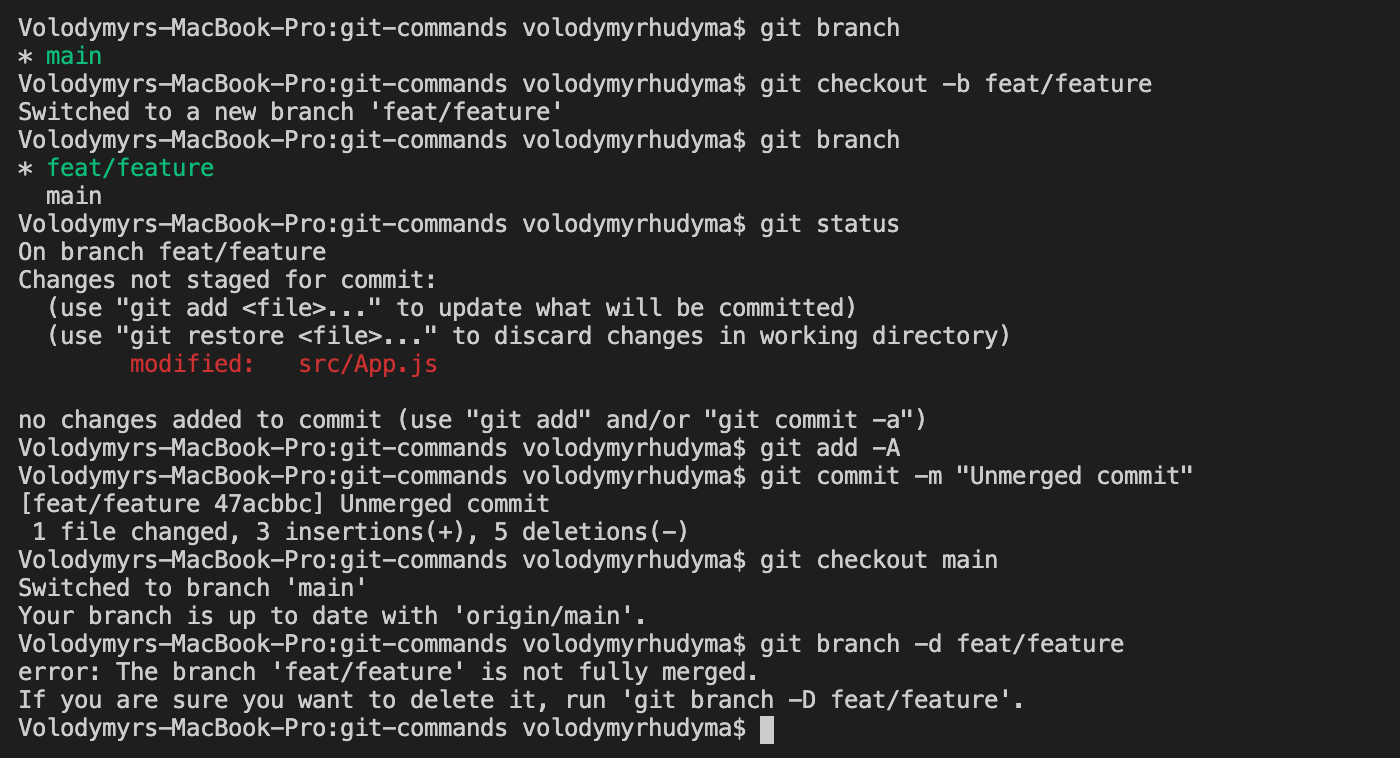
In this tutorial, you will learn how to recover your deleted commits or branches using the ` git reflog` command. It could get even worse if you are working with a bunch of other developers, as it’s easy to modify or even completely remove another person’s work, whether knowingly or inadvertently. Issues ranging from merge conflicts to accidentally deleting branches are a nightmare for many developers. Managing branches or commits in Git can be quite cumbersome. Using `git reflog` to Recover Deleted Commits
Using `git reflog` to Recover Deleted Branches


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
